Cloudy With a Chance of Credit Card Theft
by Josh Shepard on Mar 07, 2024

Executive Summary:
RADICL has recently observed an ongoing phishing campaign with the intent to steal a victim’s credit card information and other personal data such as email and physical address. What makes this campaign noteworthy is that it makes use of multiple different cloud storage providers (Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Linode Object Storage) to obfuscate phishing links and successfully bypass default phishing/spam filtering capabilities. These cloud-storage phishing links point to an HTML file that will redirect the victim through one or more adversary-controlled domains until it reaches the final phishing website. The phishing website claims that the victim has won a valuable prize, such as a Dewalt backpack. To claim it, the victim simply has to fill out a survey and then pay for the shipping costs, a nominal fee under $10 USD. Once the victim fills out their credit card details and personal information such as email and physical shipping address, that information is sent to the threat actor controlling the website and compromised.
Technical Attack Flow:
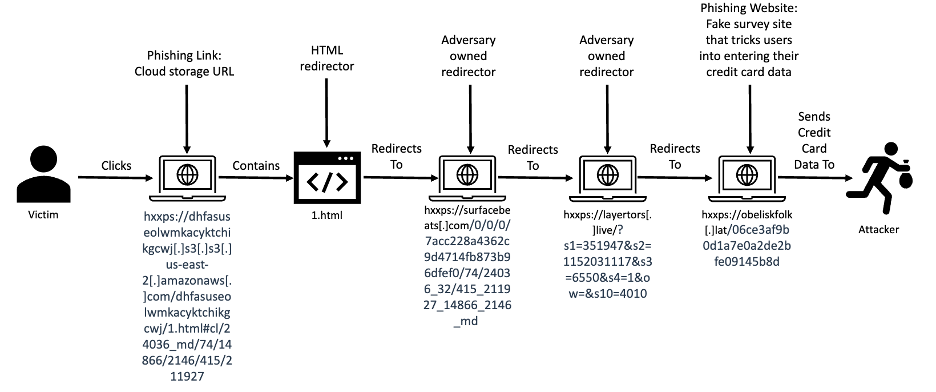
Figure 1 – Phishing Campaign Attack Flow
The phishing link used in this campaign was either a GCP, AWS, Linode, or Azure cloud storage URL that contains an HTML file that serves as a redirector to the attacker’s actual phishing site. These URLs use the below structure (broken out by service provider used):
GCP Storage Phishing URL Structure:
<random_string>.storage.googleapis.com/<optional_random_string>/<file_name>.html#<hash_part_of_url>
GCP Storage Phishing URL Example:
hxxps://artezzzzzzzzset39[.]storage[.]googleapis[.]com/artezzzzzzzzset39/1.html#cl/23028_md/72/14869/2096/474/1699344
AWS S3 Phishing URL Structure:
<random_string>.s3.<US-region>.amazonaws.com/<optional_random_string>/<file_name>.html#<hash_part_of_url>
AWS S3 Phishing URL Example:
hxxps://bjpffgozbmvmdgvhdujujsump[.]s3[.]us-east-2[.]amazonaws.com/url[.]html#cl/23356_md/14/14824/3398/415/2132211
Azure Blob Storage Phishing URL Structure:
<random_string>.blob.core.windows.net/<optional_random_string>/<file_name>.html#<hash_part_of_url>
Azure Blob Storage Phishing URL Example:
hxxps://mipho[.]blob[.]core[.]windows[.]net/mipho/url.html#cl/14315_md/2004/10360/2023/218/632788
Linode Object Storage Phishing URL Structure:
<random_string>.<US-region>.linodeobjects.com/<optional_random_string>/<file>.html#<hash_part_of_url>
Linode Object Storage Phishing URL Example:
hxxps://cwysalqybefkmthbcbluzftc[.]us-east-1[.]linodeobjects[.]com/1.html#cl/23299_md/74/14865/3425/415/603380/
Upon clicking the link, the victim's browser processes the stored HTML file. The HTML file constructs a separate URL pointing to an attacker-controlled domain by splitting the <hash_part_of_url> referenced above in the cloud storage URL structure and using the resulting values to generate a unique redirector URL as shown in in Figure 2 below:
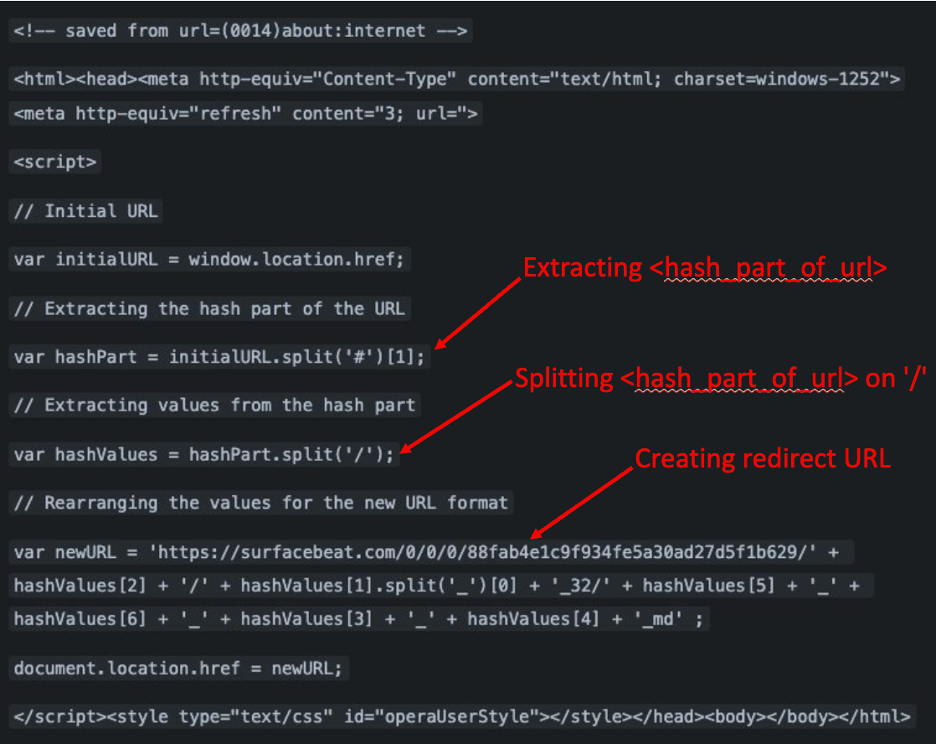
Figure 2 – Example of HTML payload found at cloud storage phishing URLs
This unique URL then redirects the victim to the final malicious website. As mentioned in the Executive Summary, the intent of this website and the overarching campaign is to trick a victim into entering credit card details and personal information such as email and physical shipping address in return for a valuable prize, as shown in Figure 3 below:
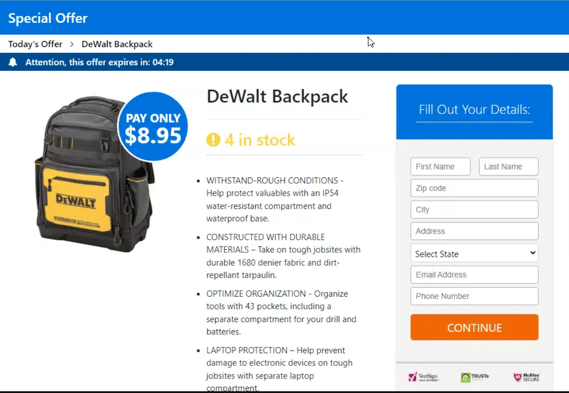
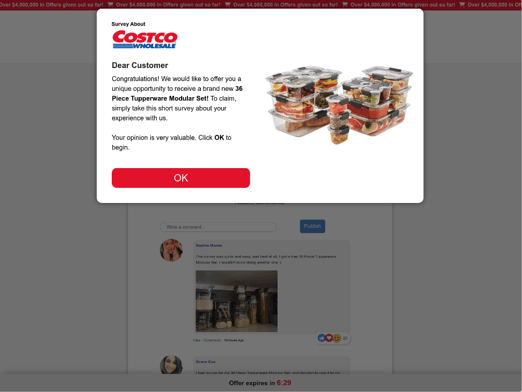
Figure 3 - Examples of phishing sites
Detection Opportunities:
Via Email Solution Logs (O365, Google Workspace, etc):
Create a detection for any URL click events involving a GCP, AWS, Linode, or Azure storage URL. If this proves too noisy, further refine the detection to search specifically for cloud storage URLs that reference an HTML file.
Via Firewall Logs:
Create a detection for any HTTP traffic directed at a cloud storage URL that references an HTML file.
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs):
Domain Names:
lumbermint[.]sbs
rangerbow[.]world
surfacebeat[.]com
jornosled[.]com
xampobrush[.]sbs
erbiumcole[.]click
kenneldress[.]lat
melodicvector[.]online
yardmolds[.]world
volantdrape[.]sbsj
ignitegate[.]click
montetrains[.]store
layertors[.]live
canopyboard[.]world
piazzaline[.]cfdl
pointerpin[.]sbs
balloonview[.]world
xomberboat[.]world
reelingplay[.]lat
leotantent[.]cfd
harlinevent[.]world
woolenvest[.]world
untrainee[.]world
latentwave[.]sbs
walkudog[.]ink
immersebind[.]lat
grillquest[.]cfd
jackethold[.]lat
erosionsite[.]sbs
driedcourt[.]click
reatincold[.]world
resistsnap[.]world
forkcrust[.]click
depictforge[.]click
gentleleaf[.]live
asparagusmud[.]cfd
zoltarzone[.]sbs
obeliskfolk[.]lat
IP Addresses:
31[.]24[.]251[.]170
172[.]99[.]173[.]54
File Names:
url[.]html
1[.]html
You May Also Like
These Related Stories

Threat Hunters Corner: A Phisher’s Love Affair With AI

Threat Hunters Corner: More_Eggs malware



No Comments Yet
Let us know what you think